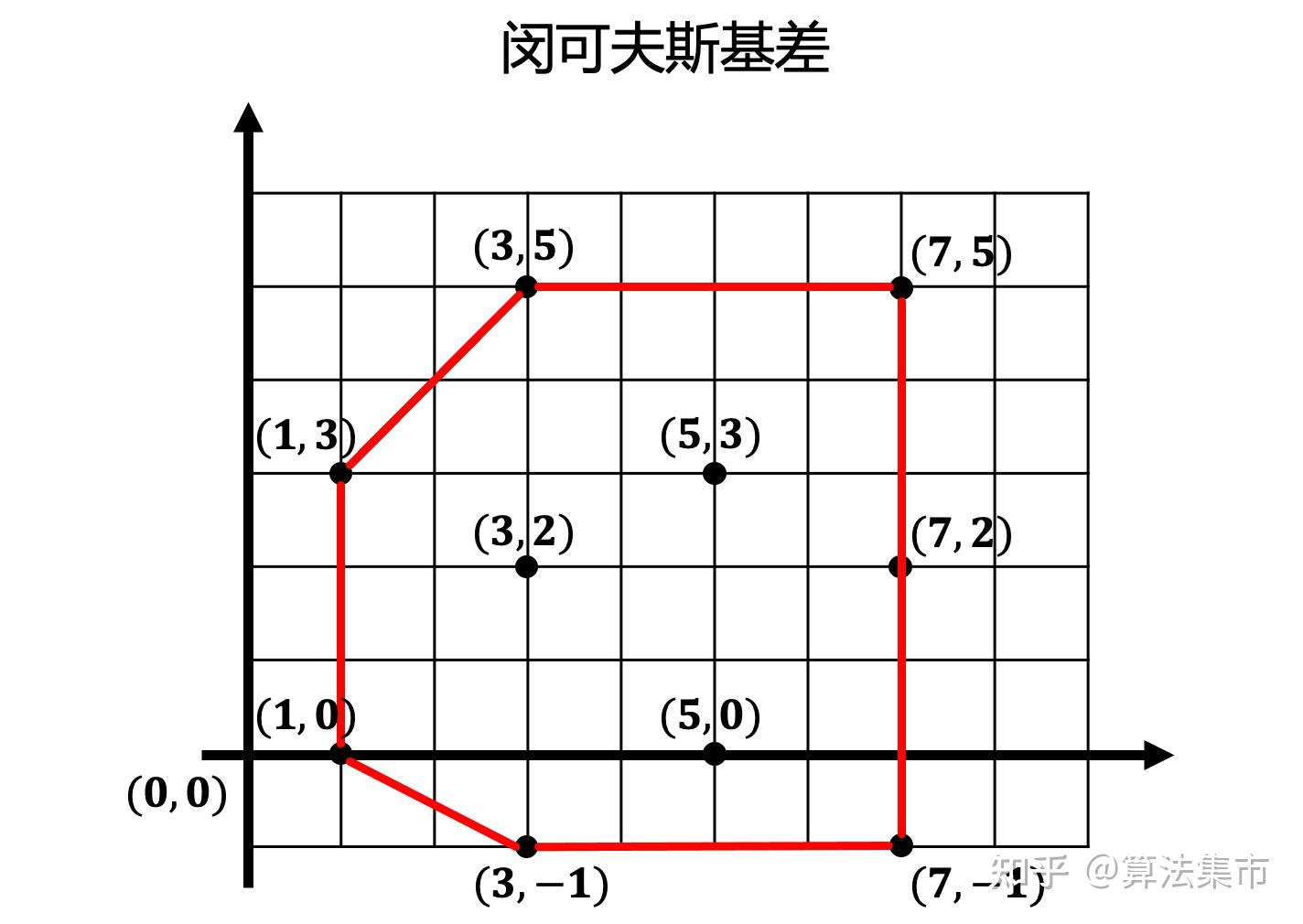
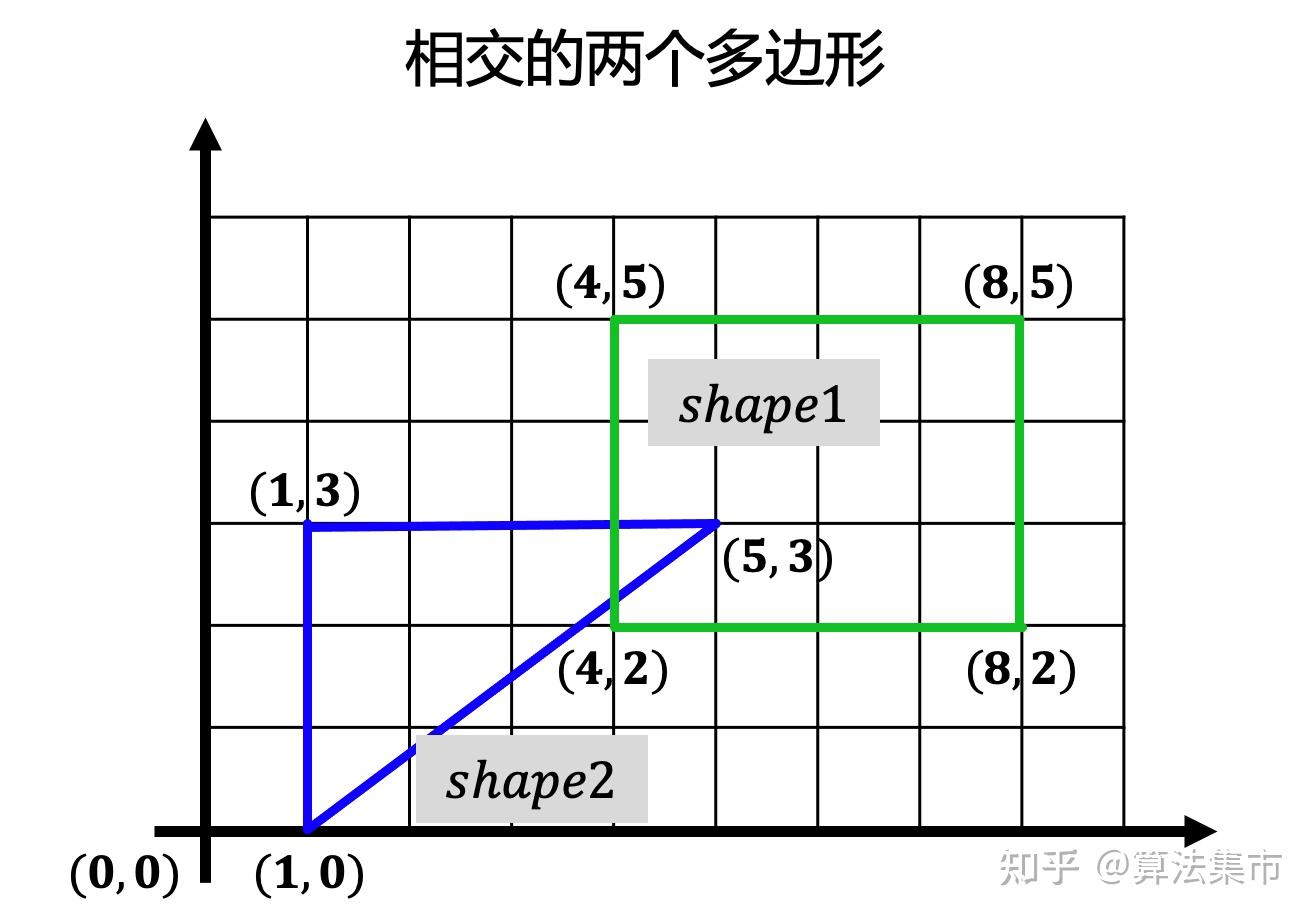
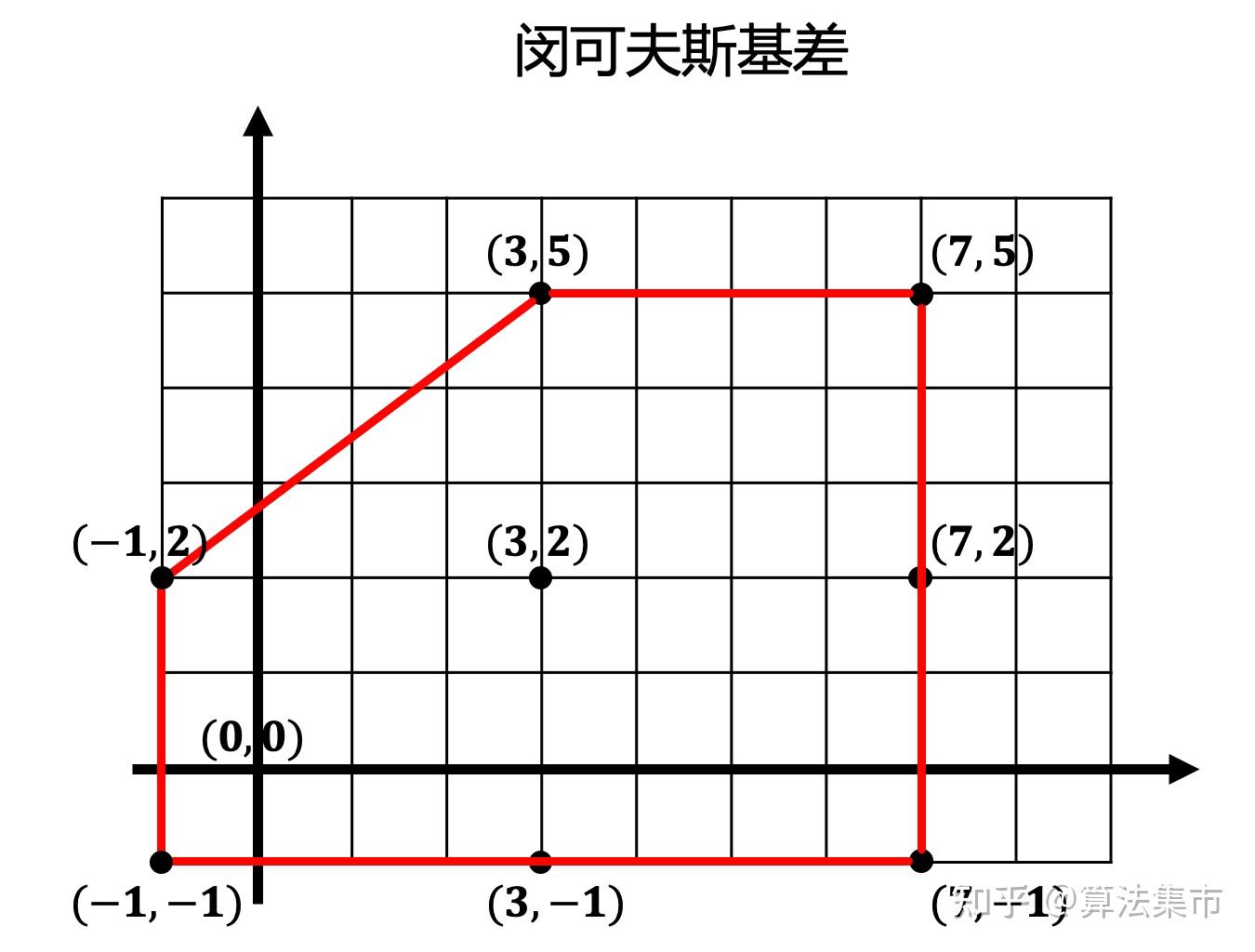
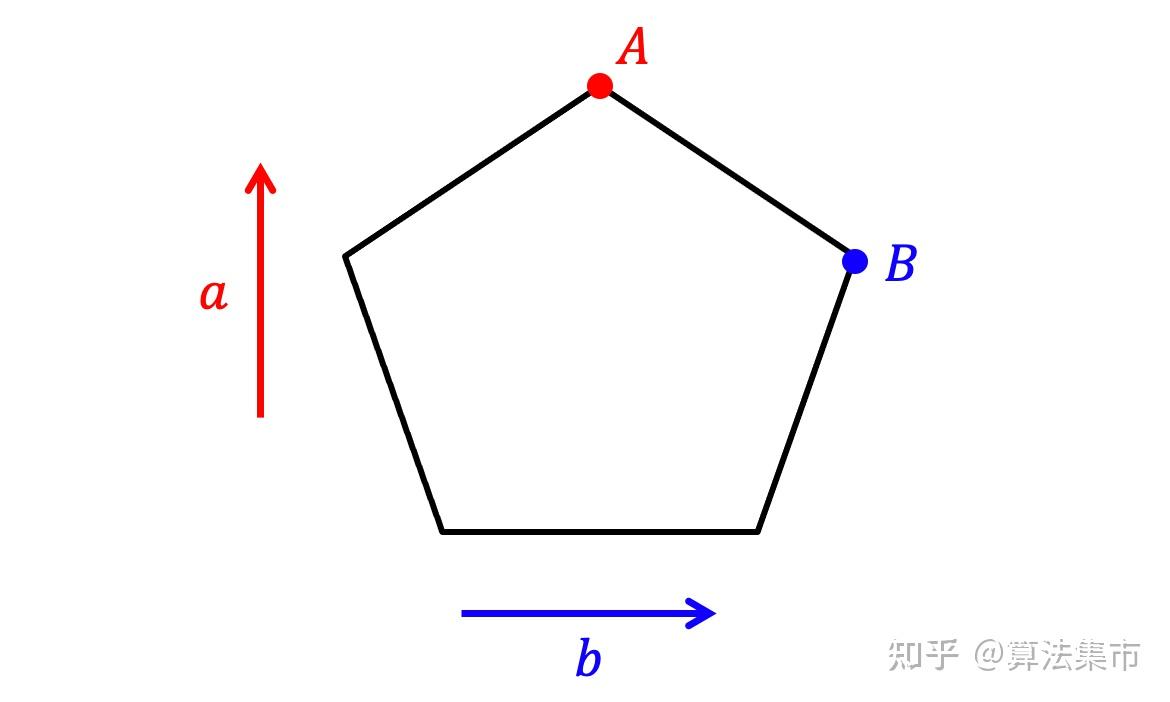
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
|
Vector = {}
Vector.__index = Vector
function Vector.new(...)
local args = {...}
return setmetatable({values = args}, Vector)
end
function Vector:dim()
return #self.values
end
function Vector:get(i)
return self.values[i+1]
end
function Vector:dot(v)
local result = 0
for i = 0, self:dim()-1 do
result = result + self:get(i) * v:get(i)
end
return result
end
function Vector:cross(v)
if self:dim() ~= 3 or v:dim() ~= 3 then
error("Cross product only for 3D vectors")
end
return Vector.new(
self:get(1)*v:get(2) - self:get(2)*v:get(1),
self:get(2)*v:get(0) - self:get(0)*v:get(2),
self:get(0)*v:get(1) - self:get(1)*v:get(0)
)
end
function Vector:length()
local sum = 0
for i = 0, self:dim()-1 do
sum = sum + self:get(i)^2
end
return math.sqrt(sum)
end
function Vector:multiply(s)
local values = {}
for i = 0, self:dim()-1 do
values[i+1] = self:get(i) * s
end
return Vector.new(unpack(values))
end
function Vector:add(v)
local values = {}
for i = 0, self:dim()-1 do
values[i+1] = self:get(i) + v:get(i)
end
return Vector.new(unpack(values))
end
function Vector:subtract(v)
local values = {}
for i = 0, self:dim()-1 do
values[i+1] = self:get(i) - v:get(i)
end
return Vector.new(unpack(values))
end
OBB = {}
OBB.__index = OBB
function OBB.new(center, halfSize, axes)
return setmetatable({
center = center,
halfSize = halfSize,
axes = axes
}, OBB)
end
function generateAxes2D(a, b)
local axes = {}
for _, axis in ipairs(a.axes) do
table.insert(axes, axis)
end
for _, axis in ipairs(b.axes) do
table.insert(axes, axis)
end
return axes
end
function generateAxes3D(a, b)
local axes = {}
for _, axis in ipairs(a.axes) do
table.insert(axes, axis)
end
for _, axis in ipairs(b.axes) do
table.insert(axes, axis)
end
for i = 1, 3 do
for j = 1, 3 do
local cross = a.axes[i]:cross(b.axes[j])
if cross:length() > 1e-6 then
table.insert(axes, cross)
end
end
end
return axes
end
function project(obb, axis)
local localCorners = generateCorners(obb)
local worldCorners = {}
for _, corner in ipairs(localCorners) do
local worldPos = obb.center:clone()
for i = 1, #obb.axes do
worldPos = worldPos:add(corner.values[i] * obb.axes[i])
end
table.insert(worldCorners, worldPos)
end
local min = math.huge
local max = -math.huge
for _, corner in ipairs(worldCorners) do
local proj = corner:dot(axis)
min = math.min(min, proj)
max = math.max(max, proj)
end
return min, max
end
function OBBIntersects(a, b)
local axes
if #a.axes == 3 and #b.axes == 3 then
axes = generateAxes3D(a, b)
else
axes = generateAxes2D(a, b)
end
for _, axis in ipairs(axes) do
local minA, maxA = project(a, axis)
local minB, maxB = project(b, axis)
if maxA < minB or maxB < minA then
return false
end
end
return true
end
|